X-ray is an electromagnetic radiation with very short wavelength and very high energy. 14122019 X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays.

Gamma Ray Definition Uses Wavelength Production Examples Facts Britannica
When you clap your hands energy in this case sound begins at.

X rays definition physics. The energy of X-ray photons are considerably. X-rays howeverhave higher frequency n and shorter wavelength l than light and radio waves. When talking about x-ray imaging however its easier to think of x-rays in terms of photons.
01022016 X-rays are produced within the X-ray machine also known as an X-ray tube. On 8 November 1895 X-rays were discovered by a German Physicist named Wilhelm Conrad Rentgen. They have a wavelength range of roughly 001 to 10 nanometers 1 nanometer 1 billionth of a meter.
The radiation frequency is key parameter of all photons because it determines the energy of a photon. Thus the arrays of atoms in a crystal can act as a diffraction grating for x rays. The wavelength of X-rays is shorter than the Ultraviolet rays and longer than Gamma rays.
These images are called diagnostic x rays. Radiographers can change the current and voltage settings on the X-ray machine in order to manipulate the properties of the X-ray beam produced. X-rays are powerful waves of electromagnetic energy.
The 1914 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Laue for the first demonstration of diffraction of x rays by a crystal. X rays are electromagnetic radiation that differentially penetrates structures within the body and creates images of these structures on photographic film or a fluorescent screen. 18052018 X rays are electromagnetic radiation that differentially penetrates structures within the body and creates images of these structures on photographic film or a fluorescent screen.
Their ability to penetrate solid objects depends on how dense the material of the object is. X-ray electromagnetic radiation of extremely short wavelength and high frequency with wavelengths ranging from about 10 8 to 10 12 metre and corresponding frequencies from about 10 16 to 10 20 hertz Hz. 31082010 X-rays are electromagnetic waves just like visible light radio waves and microwaves.
According to the currently valid definition X-rays are emitted by electrons outside the nucleus while gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus. 13 What makes x rays useful. X-rays are like radio waves and visible light electromagnetic radiation.
No external radioactive material is involved. The wavelength of x rays is in the angstrom range similar to the spacing of atoms in a crystal. An X-ray is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
A form of electromagnetic radiation similar to light but of shorter wavelength and capable of penetrating solids and of ionizing gases. Due to this small wavelength x-rays are able to pass through solid objects. Their wavelength is smaller the UV rays and they are therefore invisible to the human eye.
Theradiation can be considered as emitted in quanta photons each quantum having a welldefined energy hn where h is a physical constant Plancks constant and n is thefrequency. 14122019 X-rays also known as X-radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation no rest mass no charge of high energies. Different X-ray beam spectra are applied to different body parts.
X rays have a frequency ranging from 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz. 26122020 X rays are a kind of super-powerful version of ordinary light. X-rays are high-energy photons with short wavelengths and thus very high frequency.
Waves like those found in the ocean are the movement of energy. These images are called diagnostic x rays. A higher- energy form of electromagnetic radiation that travel at the speed of light in straight lines just like light waves do.
The distinction between X-rays and gamma rays is not so simple and has changed in recent decades. Such radiation having wavelengths in.
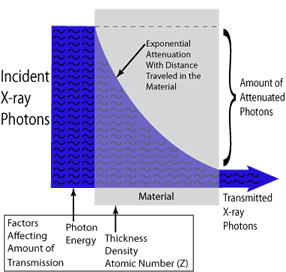
Nondestructive Evaluation Physics X Ray

Frcr Physics Lectures Diagnostic Radiology Ppt Video Online Download

Anode Heel Effect X Ray Tube Youtube

What Is X Ray Production X Ray Tube Definition
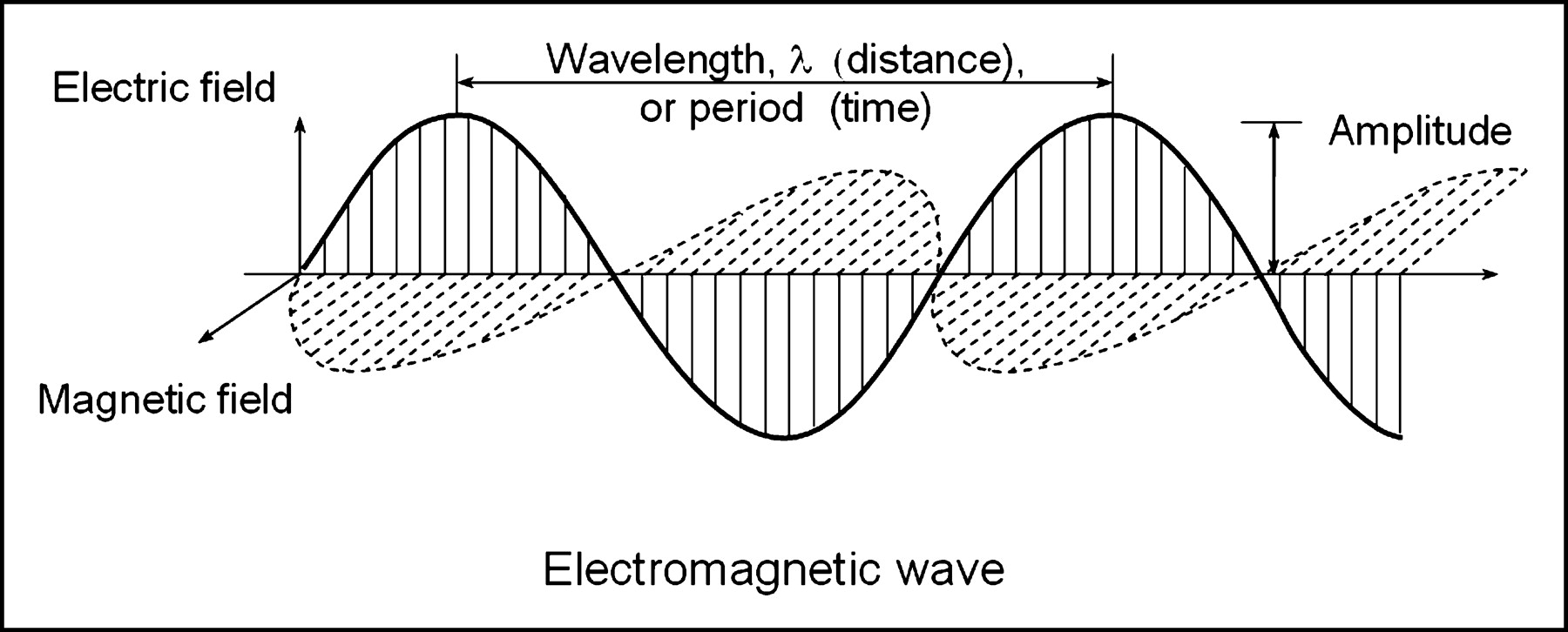
X Ray Imaging Physics For Nuclear Medicine Technologists Part 1 Basic Principles Of X Ray Production Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology
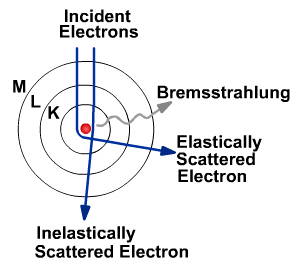
Nondestructive Evaluation Physics X Ray



0 comments:
Post a Comment