The area of the A rectangle is d V1Δt. Y c 4r 3ˇ C 4r r 3ˇ 5.
V2 - V1 Δt.
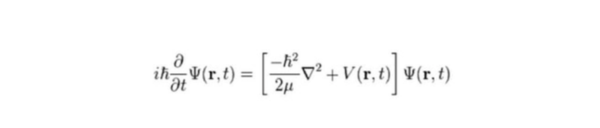
Big 3 physics equations. The 5 Key equations of accelerated motion apply to motion with uniform acceleration. This is second equation of kinematics where s is displacement not distance note it u is initial velocity a is uniform acceleration and t is time. Physics 11 - 25 The Big 3 Kinematics Equations - YouTube.
Y c r 2 C r r 2 6. Center of mass xCM. Equation 3 is d V1Δt aΔt.
Now for third kinematics equation square on both side first equation as v. The diffusion equation the wave equation and Laplaces equation. An objects motion can be described using words diagrams numbers graphs and equations.
Wave x t wave average velocity x displacement t elapsed time. The area of the B triangle is d. 3 C h 3 h 3.
Well do the cool geometric derivation first. If values of three variables are known then the others can be. Only one will have exactly these five variables.
The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi. Y c 3r 8 C r 3r 8 7. T elapsed time.
They involve the variables for displacement initial velocity final velocity acceleration and time interval. θ angle between incline and horizontal. Wien displacement constant b 29.
There are a couple ways to derive the equation. By the end I expect that answer to be 29 ms. A cm F ext M Impulse.
Use this formula when you dont have vf. Understand the physical meaning of numerical quantities. Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another.
M P m i v cm P m iv i M. And the student to be able to explain whether this is a car on the freeway a cruising airplane or a sprinter on the track team. Therefore the displacement is equal to the area of the area of the A rectangle plus the B triangle.
X x 0 v 0 t. J R Fdt p Collision. P cm Mv cm.
Theres a cool geometric derivation and a less exciting plugging-and-chugging derivation. 25032018 s ut 12at. XCM m₁x₁ m₂x₂ m₃x₃ m₁ m₂ m₃ Center of gravity xCG.
Physics 11 - 25 The Big 3 Kinematics Equations. Motion of the CM. When solving uniform acceleration choose which equations to use based on the given and required variables for the question.
In the first month of class a student might write down an answer as 2943872743. The height of CM from the base is h4 for the solid cone and h3 for the hollow cone. U at.
Consider an object that starts with a velocity and maintains constant acceleration to a final velocity of as seen in the graph below. 22102010 Big Five Equations 3 Blog 10 How to derive equation number three from a graph. The Big Four - Kinematic Equations Kinematics the topic of the current unit is the science of describing the motion of objects.
Simplify this equation. 06062008 Often a mathematical physics class will focus on the big three partial differential equations of physics. The most commonly used of all equations are the four kinematic equations - affectionately known as the big four.
XCG w₁x₁ w₂x₂ w₃x₃ w₁ w₂ w₃ In a uniform gravitational field constant g. The 4th edition of Intermediate Physics for Medicine and Biology provides a gentle introduction to each of these equations. Vf final velocity that is another definition of the average velocity which works where letter a is constant.
In this case we need Equation 3. 103 m K. 25042014 Now look at the Big Five Equations.
Centripetal acceleration ac ac vr. Start studying Kinematics Equations The Big Three Burke Physics. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Each equation contains four variables. Y c 2r ˇ C 2r r ˇ 4.
Equations That Changed The Course Of History Cosmos Magazine

0 comments:
Post a Comment