Heat Generated Formula Physics
When these three conditions are merged the resulting formula is like this. Heat Transfer Formula Heat a measure of thermal energy can be transferred from one point to another.

Heating Effects Of Electric Current And Its Applications Concepts
In an isolated system given heat is always equal to taken heat or heat change in the system is equal to zero.
Heat generated formula physics. The amount of heat produced by the heater is calculated as follows. If two objects having different temperatures are in contact heat transfer starts between them. Hence the heat generated with repect to time is just Fv - in Watts.
230V 575 Ω 4A 920J 920W. To know more about Joules law of thermodynamics and solved examples you can visit us BYJUS. Calculations of Heat Transfer Conservation of energy theorem is also applied to heat transfer.
Electrical energy and power. Substituting the values in the equation we get. Joules first law also known as the JouleLenz law states that the power of heating generated by an electrical conductor is proportional to the product of its resistance and the square of the current.
230V 115 Ω 2A 460J 460W Difference in resistance. The actual heat generated will be the same if power is the same but the heat we feel depends upon the material. 460V 575 Ω 8A.
Joules J ampere2A2. The higher the current the larger the amount of heat generated. The amount of current I.
I think this is correct. Equation 19 is the three-dimensional form of Fouriers law. Endgroup Siddharth Venu Apr 6 16 at 1529.
22052019 The heat conduction equation is a partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat or the temperature field in a given body over time. Now applying the heat formula c fracQmDelta T rearranging the formula Q mcDelta T Q 1 times 045 times 103 times 450 2025 J. This equation is called the Joules equation of electrical heating.
Heat flows from the point of higher temperature to one of lower temperature. 230V 230 Ω 1A 230J 230J Difference in resistance. Determine how much heat energy is lost if 50 Kg water is cooled from 600degreeC to 200degreeC.
Detailed knowledge of the temperature field is very important in thermal conduction through materials. Heat generated per second Heat H V. It is valid for homogeneous isotropic materials for which the thermal conductivity is the same in all directions.
115V 575 Ω 2A 230J 230J Difference in resistance. Heat Transfer Formula Heat transfer is a process is known as the exchange of heat from a high-temperature body to a low-temperature body. Q 10 2.
The amount of heat given is equal to the amount of heat taken. Equation 19 states that the heat flux vector is proportional to the negative of the temperature gradient vector. Hence the heating effect produced by an electric current I through a conductor of resistance R for a time t is given by H I 2 Rt.
As a system temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particle in the system also increases. The heat content Q of an object depends upon its specific heat c and its mass m. Express the heat gained by the water in terms of the mass of the water the specific heat of water the initial temperature of the water and the final temperature.
Specific heat of water is given as C 42 times103 JKg-1. 24042012 The heat generated due to the flow of current is proportional to the time of current flowing when the electrical resistance and the amount of current is constant. 06042016 begingroup VIR PIRI therefore PI2R You can do the same using this formula and the same answer will come.
Q cold m W c W T f 200C. As we know heat is a kinetic energy parameter included by the particles in the given system. Fundamentally it comes down to the conservation of energy since we already know the initial velocity of both objects by simply measuring the velocities of the objects just after the collision say v_1 for object 1 and v_2 for object 2 we can calculate the amount of energy converted to heat by simply using m_1v2 m_1v_12 m_2v_22 Heat.
Note that Q hot 0 and Q cold 0 and that they must sum to zero because the heat lost by the hot pan must be the same as the heat gained by the cold water. T Power given by the device P V. Joule heating also known as resistive resistance or Ohmic heating is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.
60 54000000 J or 54 MJ. I or P H t Reason for the change in power. 06062008 In this case the power of the applied force is Fv which here is just Fv and by conservation of energy the only energy transfer is to the internal energy of the blockfloor.
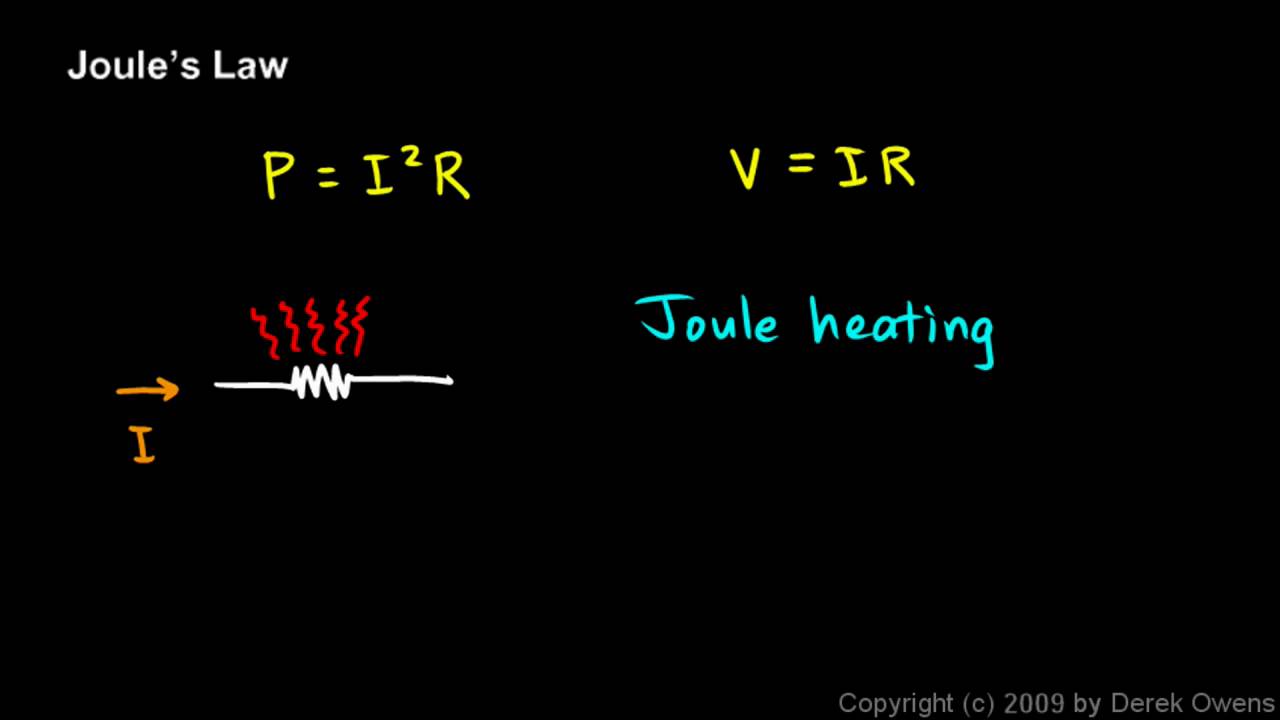
Physics 13 3 2a Joule S Law Youtube

Heating Effects Of Electric Current And Its Applications Concepts
Thermal Energy From Friction Video Khan Academy

Heat Engines Thermal Efficiency Energy Flow Diagrams Thermodynamics Physics Problems Youtube
What Is Thermal Energy Article Khan Academy

How To Calculate Specific Heat 6 Steps With Pictures Wikihow

5 Ways To Calculate Joules Wikihow




Post a Comment for "Heat Generated Formula Physics"